Understanding Heart Failure: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options
Table of Contents
Introduction:
Heart failure is a dangerous medical illness that manifests as a variety of symptoms and problems due to the heart’s inability to pump blood efficiently. It is essential to comprehend the origins, signs, and available treatments for heart failure in order to manage the illness and enhance your quality of life.
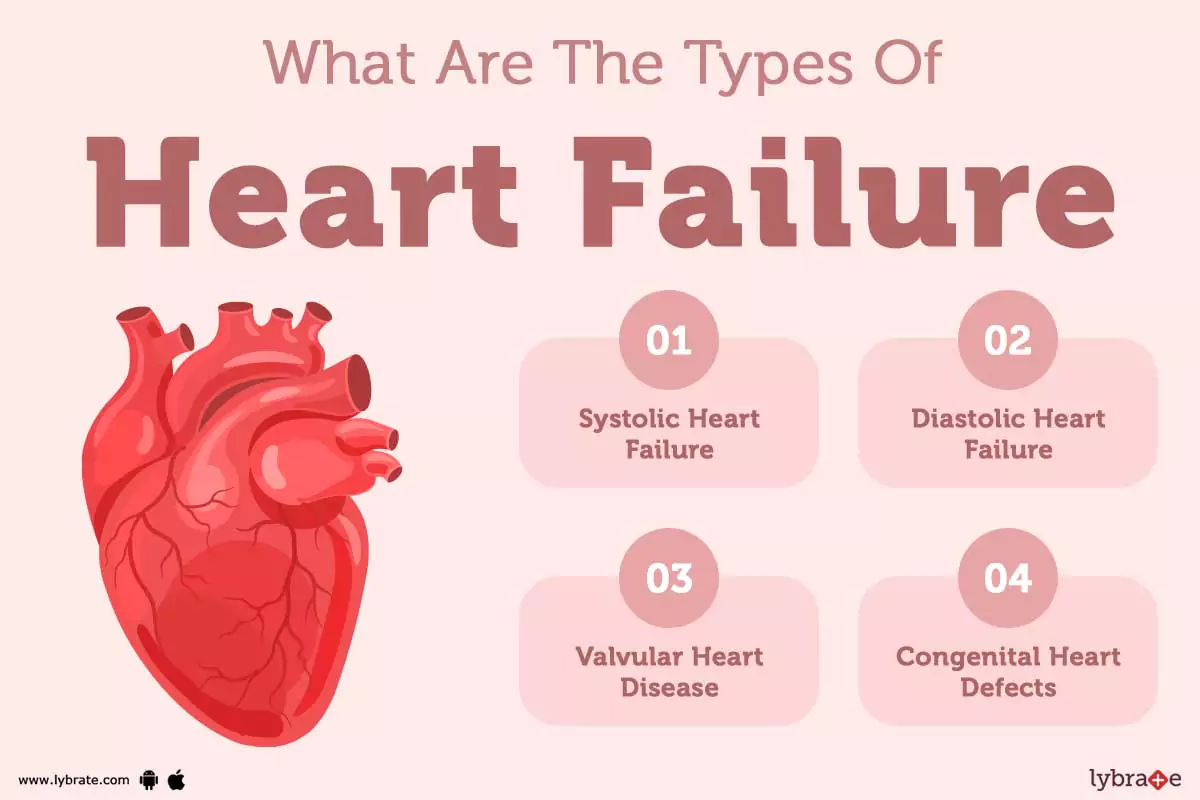
Types of Heart Failure
Left-sided heart failure
The heart’s pumping action moves oxygen-rich blood from the lungs to the left atrium, then on to the left ventricle, which pumps the blood to the rest of the body. The left ventricle supplies most of the heart’s pumping power, so it’s larger than the other chambers and essential for normal function. In left-sided or left-ventricular heart failure, the left side must work harder to pump the same amount of blood. The percentage of blood the heart can pump with each beat is measured by a unit called ejection fraction, or EF. A normal left ventricle ejects about 55% to 60% of the blood in it.
There are two types of left-sided heart failure:
- Systolic failure: The left ventricle loses its ability to contract normally. The heart can’t pump with enough force to push enough blood into circulation. This is also known as heart failure with reduced ejection, or HFrEF. When this occurs, the heart is pumping less than or equal to 40% EF.
- Diastolic failure: The left ventricle loses its ability to relax normally because the muscle has become stiff. The heart can’t properly fill with blood during the resting period between each beat. This is also known as heart failure with preserved ejection, or HFpEF. When this occurs, the heart is pumping greater than or equal to 50%. EF heart failure with mid-range ejection fraction (HFmrEF) is a newer concept. In this type of heart failure, the left ventricle pumps between 41% and 49% EF. This places people with HFmrEF between the HFrEF and HFpEF groups.
Right-sided heart failure
The heart’s pumping action moves “used” blood that no longer has oxygen in it back to the right atrium and onto the right ventricle. The right ventricle then pumps the blood back out of the heart and into the lungs to be replenished with oxygen. Right-sided or right-ventricular heart failure usually occurs as a result of left-sided failure. When the left ventricle fails and can’t pump enough blood out, increased fluid pressure is transferred back through the lungs. This damages the heart’s right side. When the right side loses pumping power, blood backs up in the body’s veins.
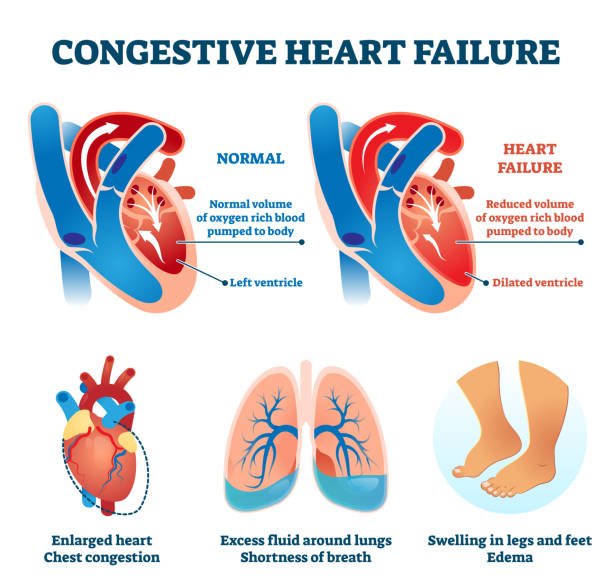
Congestive heart failure
Congestive heart failure, sometimes called CHF, requires quick medical attention. However, sometimes doctors use the terms congestive heart failure and Left-sided heart failure The heart’s pumping activity moves oxygen-rich blood from the lungs to the cleared-out chamber and, at that point on to the cleared-out ventricle, which pumps the blood to the rest of the body. The cleared-out ventricle supplies most of the heart’s pumping control, so it’s bigger than the other chambers and basic for typical function. In left-sided or cleared-out ventricular heart disappointment, the cleared-out side must work harder to pump the same sum of blood. The rate of blood the heart can pump with each beat is measured by a unit called launch division, or EF. An ordinary cleared-out ventricle launches almost 55% to 60% of the blood in it.
There are two sorts of left-sided heart failure:
Systolic disappointment: The cleared-out ventricle loses its capacity to contract regularly. The heart can’t pump with enough force to thrust sufficient blood into circulation. Typically moreover known as heart disappointment with decreased discharge, or HFrEF. When this happens, the heart is pumping less than or rises to 40% EF.
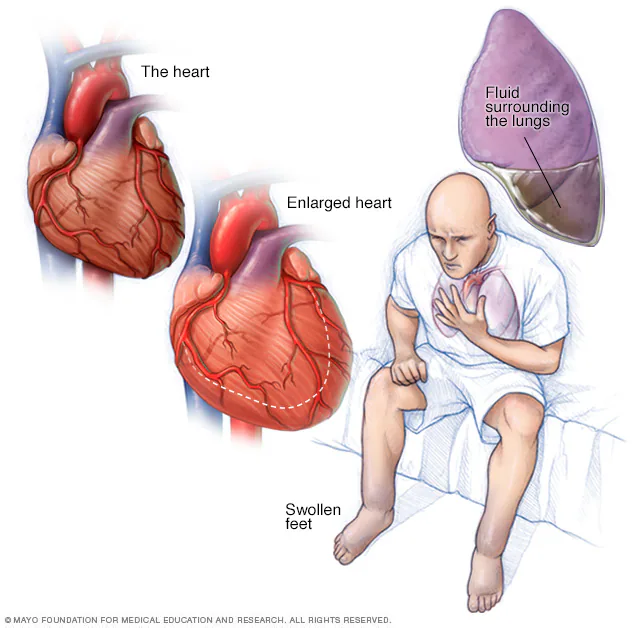
Diastolic disappointment: The cleared-out ventricle loses its capacity to unwind regularly since the muscle has become hardened. The heart can’t appropriately fill with blood amid the resting period between each beat. This is often known as heart disappointment with protected ejection, or HFpEF. When this happens, the heart is pumping more noteworthy than or rises to 50%. EF heart disappointment with mid-range discharge division (HFmrEF) may be a concept. In this sort of heart disappointment, the cleared-out ventricle pumps between 41% and 49% EF. This places individuals with HFmrEF between the HFrEF and HFpEF groups. As the bloodstream out of the heart moderates, blood returning to the heart through the veins backs up. This causes blockage within the body’s tissues. Often swelling, known as edema, comes about. Most regularly there’s swelling within the legs and lower legs, but it can happen in other parts of the body, too. In some cases liquid collects within the lungs and meddling with breathing, causing shortness of breath, particularly when an individual is lying down. This is often pneumonic edema. In case cleared out untreated, aspiratory edema can cause respiratory distress.Heart disappointment moreover influences the kidneys’ capacity to arrange sodium and water. This comes about in more blood volume. This held water to increase swelling within the body’s tissues.
Causes of Heart Failure:
The following are some of the variables that may lead to the development of heart failure:
- Coronary artery disease
- High blood pressure
- Previous heart attack
- Cardiomyopathy
- Heart valve disorders
- Diabetes
- Obesity
- Smoking
- Excessive alcohol consumption
Symptoms of Heart Failure:
- Although each person’s symptoms of heart failure are unique, typical indications might be:
- breathing problems, especially after moving or sleeping
- Weakness and exhaustion
- abdomen, ankles, or legs swelling
- accelerated or irregular heart rate
- Persistent coughing or wheezing
- Reduced ability to exercise
- Sudden weight gain
- Difficulty concentrating or confusion
Treatment Options for Heart Failure:
- Improving heart function, reducing symptoms, and preventing consequences are the goals of heart failure treatment. Treatment choices might include the following, depending on how severe the illness is:
- drugs such aldosterone antagonists, beta-blockers, diuretics, and ACE inhibitors
- Modifications to one’s lifestyle include eating a balanced diet, getting regular exercise, giving up smoking, and consuming less alcohol.
- Programs for cardiac rehabilitation
- Pacemakers and implanted cardioverter-defibrillators (ICDs) are examples of device treatment.
- surgical treatments such cardiac valve replacement or repair or coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG)
FAQs:
Q. Is heart failure preventable?
A healthy lifestyle can greatly lower your risk of heart failure, even if prevention may not always be achievable.
Q. What is the heart failure prognosis?
A lot of people with heart failure are able to have active, satisfying lives if they receive the right care.
Q. Is a heart attack and heart failure the same thing?
A: No, a heart attack develops when blood supply to the heart is obstructed, whereas heart failure arises from the heart’s inability to pump blood efficiently.
Conclusion
heart failure is a dangerous illness that needs constant attention and care. Knowing the causes, signs, and available treatments for heart failure can enable you to take preventative measures to enhance your general and cardiac health.




