Understanding Depression and Anxiety: Breaking the Silence
Depression and anxiety are two common mental health conditions that affect millions of people worldwide. Despite their prevalence, there is still a stigma surrounding these disorders, making it difficult for individuals to seek help and support. In this blog post, we will explore what depression and anxiety are, their symptoms, and the importance of seeking professional assistance.

What is Depression?
Depression is further than just feeling sad or down. It is a persistent and overwhelming feeling of sadness, hopelessness, and emptiness that affects a person’s daily life. Symptoms of depression can include:
- Changes in appetite and weight
- Trouble sleeping or excessive sleeping
- Feeling tired and lacking energy
- Difficulty concentrating or making decisions
- Thoughts of death or suicide
Depression can be caused by a combination of inheritable, natural, environmental, and cerebral factors. It is important to remember that depression is not a sign of weakness or a character flaw. It is a medical condition that can be effectively treated with therapy, medication, or a combination of both.

Understanding Anxiety
Anxiety is a normal reaction to stress, but when it becomes excessive and interferes with daily life, it may be classified as an anxiety disorder. Symptoms of anxiety can include:
- Excessive worrying or fear
- Feeling restless or on edge
- Difficulty controlling worrying thoughts
- Physical symptoms such as rapid heartbeat, sweating, and trembling
- Avoidance of certain situations or places
Anxiety disorders can be caused by a combination of genetic, environmental, and psychological factors. It is essential to recognize that anxiety is treatable, and seeking professional help is crucial in managing and overcoming anxiety.
Understanding Depression and Anxiety Symptoms
Introduction:
Feeling down or anxious from time to time is a normal part of life. However, when these feelings become persistent and start interfering with daily functioning, it may indicate a deeper issue. Depression and anxiety are common internal health conditions that affect millions of people worldwide. In this article, we will explore the symptoms of depression and anxiety, shedding light on what individuals experience and offering guidance on seeking help.

Depression and Anxiety: A Closer Look
Depression Symptoms:
Depression is more than just feeling sad; it encompasses a range of emotional, physical, and behavioral symptoms. Some common signs of depression include:
- Persistent sadness or emptiness.
- Sleep disturbances, such as insomnia or oversleeping.
- Fatigue or lack of energy.
- Significant weight changes.
- Feelings of worthlessness or excessive guilt.
- Difficulty concentrating or making decisions.
- Recurring thoughts of death or suicide.
It is important to note that not everyone with depression experiences these symptoms in the same way. The severity and duration of symptoms may vary from person to person. Seeking professional help is pivotal for accurate opinion and applicable treatment.
Anxiety Symptoms:
Anxiety, on the other hand, manifests in excessive worry, fear, and nervousness. The symptoms of anxiety can be both emotional and physical, and they can significantly impact daily life. Some common anxiety symptoms include: - Excessive worrying about various aspects of life.
- Restlessness or feeling on edge.
- Irritability.
- Muscle tension or trembling.
- Racing thoughts or feeling overwhelmed.
- Sweating or shortness of breath.
- Trouble sleeping.
- Avoidance of situations that trigger anxiety.
- Just like depression, anxiety affects individuals differently. It can range from mild to severe, and individuals may experience a combination of symptoms.
Seeking Help: Where to Start If you or someone you know is experiencing symptoms of depression or anxiety, it is essential to seek professional help. Mental health professionals, such as psychologists or psychiatrists, are trained to diagnose and provide appropriate treatment for these conditions. They can offer various interventions, including therapy and medication, based on the individual’s needs.
Additionally, engaging in self-care practices can also contribute to managing depression and anxiety symptoms. Then are some strategies that may help:
- Regular exercise, such as walking, yoga, or dancing, can boost mood and reduce symptoms.
- Engaging in activities you enjoy can provide a sense of pleasure and fulfillment.
- Seeking support from friends and loved ones can help alleviate feelings of isolation.
- Rehearsing relaxation ways, similar as deep breathing or contemplation, can reduce anxiety.
Medications for Depression
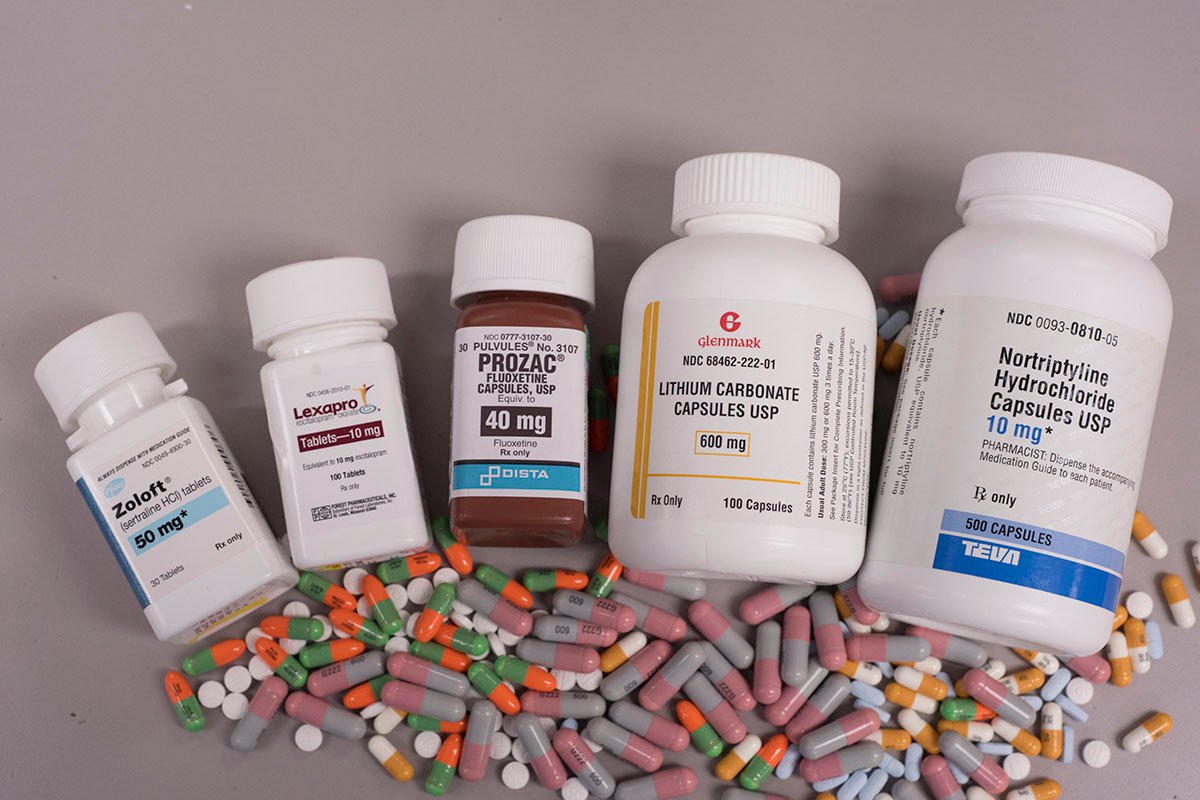
Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs)
One common type of antidepressant medication is SSRIs. These drugs work by increasing the levels of serotonin, a neurotransmitter that affects mood regulation, in the brain. SSRIs are considered a first-line treatment for depression due to their effectiveness and relatively low side effect profile.
Commonly prescribed SSRIs include:
- Prozac (Fluoxetine)
- Zoloft (Sertraline)
- Lexapro (Escitalopram)
- Paxil (Paroxetine)
Serotonin-Norepinephrine Reuptake Inhibitors (SNRIs)
SNRIs are another class of antidepressants that work by increasing the levels of both serotonin and norepinephrine, another neurotransmitter involved in mood regulation. This dual mechanism of action can be particularly beneficial for individuals who do not respond well to SSRIs alone.
Examples of SNRIs commonly prescribed for depression include:
- Cymbalta (Duloxetine)
- Effexor (Venlafaxine)
- Pristiq (Desvenlafaxine)
Atypical Antidepressants
Atypical antidepressants refer to a group of medications that do not fit into the traditional antidepressant categories but still effectively treat depression. These drugs target different neurotransmitters and include:
- Wellbutrin (Bupropion)
- Remeron (Mirtazapine)
- Trazodone (Oleptro)
Medications for Anxiety
Benzodiazepines
Benzodiazepines are a class of medications that act as sedatives, calming the central nervous system and reducing anxiety symptoms. They are typically prescribed for short-term use due to their potential for dependence and tolerance.
Examples of commonly prescribed benzodiazepines for anxiety include:
- Xanax (Alprazolam)
- Valium (Diazepam)
- Ativan (Lorazepam)
Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs)
In addition to being used for depression treatment, SSRIs are also effective in managing various anxiety disorders. The same drugs mentioned for depression earlier, such as Prozac and Zoloft, can be prescribed for anxiety as well.
Buspirone
Buspirone is an antianxiety medication that is often prescribed for generalized anxiety disorder. It works by stimulating serotonin receptors in the brain and has a low potential for addiction and abuse.
Beta-Blockers
While not typically considered traditional anxiety medications, beta-blockers may be prescribed to manage physical symptoms of anxiety, such as rapid heart rate, trembling, and sweating. These medications are often helpful for situations that trigger performance anxiety, such as public speaking or job interviews.
Self-Care and Coping Strategies
In addition to professional help, there are several self-care strategies that can help manage depression and anxiety:
- Engage in regular physical exercise
- Maintain a healthy diet
- Get enough sleep
- Avoid alcohol and drug use
Remember, self-care is not selfish. It is important to prioritize self-care and engage in activities that promote relaxation and happiness.
Depression and Anxiety Test: Assess Your Mental Well-being
Introduction
Mental health is a topic that cannot be ignored in today’s fast-paced and stressful world. Depression and anxiety are two common mental health disorders that can significantly impact a person’s quality of life. Identifying these conditions early on is crucial to ensure timely intervention and support. One effective way to assess your mental well-being is through taking a depression and anxiety test. This article will discuss the importance of such tests, how they work, and provide some valuable insights into managing depression and anxiety.
What is a Depression and Anxiety Test?
A depression and anxiety test is a tool designed to assess the presence and severity of symptoms related to these mental health disorders. These tests typically use validated questionnaires that ask individuals about their feelings, behaviors, and overall emotional well-being. By answering a series of questions, individuals can gain valuable insights into their mental state and identify if they are at risk of experiencing depression or anxiety.
Importance of Taking a Depression and Anxiety Test
- Early Detection: A depression and anxiety test can help in early detection of these mental health disorders, enabling individuals to seek timely treatment and support. Early intervention is crucial in managing and improving mental well-being.
- Self-Awareness: Taking a test allows individuals to reflect on their emotional well-being and gain a deeper understanding of their mental health. It gives them the opportunity to identify any symptoms they may be experiencing and take necessary steps towards seeking help.
- Validation: Many individuals may be unsure if what they are feeling is related to depression or anxiety. Taking a test can provide validation and clarity, helping them understand that what they are experiencing is not uncommon and can be addressed.
- Monitoring Progress: For individuals who are already undergoing treatment or therapy for depression or anxiety, regular testing can help monitor their progress and assess the effectiveness of the interventions being implemented.
How Does a Depression and Anxiety Test Work?
Depression and anxiety tests typically consist of a series of questions that assess different aspects of mental health. These questions can cover areas such as mood, energy levels, sleep patterns, social interactions, and concentration abilities. The answers provided are then scored, and the results are interpreted based on established guidelines.
It is important to note that these tests are not definitive diagnostics but rather indicators of potential mental health issues. If the test results suggest the presence of depression or anxiety, it is advisable to seek professional help for a thorough evaluation and diagnosis.
Managing Depression and Anxiety
- Seek Professional Help: If you suspect you may be experiencing depression or anxiety, it is important to seek professional help. Mental health professionals, such as therapists or psychiatrists, are trained to provide the necessary support and guidance for managing these conditions.
- Practice Self-Care: Engaging in self-care activities, such as exercise, practicing mindfulness, getting enough sleep, and maintaining a healthy diet, can significantly contribute to managing depression and anxiety.
- Build a Support System: Surrounding yourself with supportive and understanding individuals can make a significant difference in managing mental health challenges. Reach out to friends, family, or support groups who can provide a listening ear and offer assistance when needed.
- Explore Therapeutic Interventions: Various therapeutic interventions, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), mindfulness-based stress reduction (MBSR), or medication, can be beneficial in managing depression and anxiety. Consult with a mental health professional to determine the most suitable approach for you.
Breaking the Silence
By raising awareness and breaking the silence surrounding depression and anxiety, we can create a more supportive and understanding society. Let us spread compassion, empathy, and knowledge about mental health. Together, we can make a difference and provide a safe space for those struggling with depression and anxiety.
If you or someone you know is struggling with depression or anxiety, please remember that help is available.

