Type 2 Diabetes: Understanding the Silent Killer
Introduction:
In present’s fast- paced world, our health frequently takes a backseat. One such health condition that is slowly becoming an epidemic is Type 2 diabetes. This chronic disease affects millions of people worldwide and is characterized by high blood sugar levels. In this article, we will explore:
- Means
- Causes
- Symptoms
- Treatment
- Type 2 Diabetes Food List
- Diet
- Type 2 Diabetes range
- Age
- Type 2 Diabetes food chart

Type 2 Diabetes: What is it?
Type 2 diabetes is a metabolic disorder that affects the body’s ability to regulate blood sugar levels. Unlike Type 1 diabetes, where the body does not produce enough insulin, Type 2 diabetes occurs when the body becomes resistant to the insulin it produces. Insulin is responsible for moving glucose from the bloodstream into the cells, where it is converted into energy.
Causes of Type 2 Diabetes:
The exact cause of Type 2 diabetes is not fully understood, but several risk factors contribute to its development. These include:
1. Obesity: Excess weight, especially around the waist, increases the risk of developing Type 2 diabetes. Being overweight puts pressure on the body’s cells, leading to insulin resistance.
2. Sedentary Lifestyle: Lack of physical activity reduces the body’s ability to utilize insulin effectively, making it more susceptible to Type 2 diabetes
3. Genetics: Family history plays a significant role in determining the risk of developing Type 2 diabetes. If your parents or siblings have the condition, your chances of developing it increase.
4. Age: The risk of developing Type 2 diabetes increases with age, especially after the age of 45. This is due to the natural decline in insulin sensitivity as we grow older.
5. Unhealthy Diet: Consuming a diet high in processed foods, sugary drinks, and unhealthy fats increases the risk of Type 2 diabetes. A diet low in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains also contributes to its development.
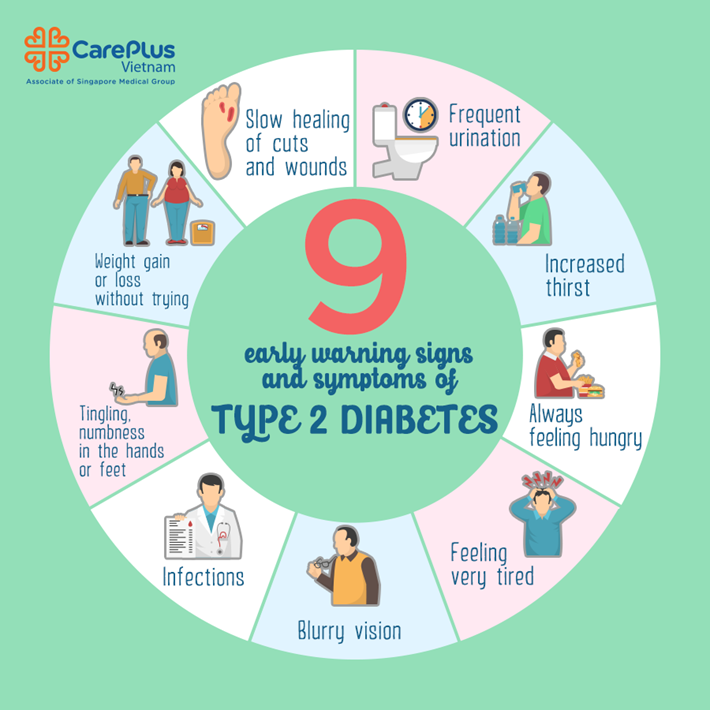
Symptoms of Type 2 Diabetes?
Type 2 diabetes often develops gradually, and some individuals may not experience any noticeable symptoms in the early stages. However, common symptoms include:
1. Frequent Urination: Increased blood sugar levels lead to excess glucose being eliminated through urine, causing frequent urination.
2. Increased Thirst: As the body loses more fluid through urine, it leads to dehydration and increased thirst.
3. Fatigue: When glucose cannot enter the cells and be converted into energy, it results in fatigue and lack of energy.
4. Slow Healing: High blood sugar levels can impair the body’s ability to heal wounds and infections.
5. Blurred Vision: Elevated blood sugar levels can cause fluid to be pulled from the lenses of the eyes, resulting in blurred vision.
Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes:
Lifestyle Changes to Manage Type 2 Diabetes
- Dietary Modifications: One of the primary aspects of managing type 2 diabetes is modifying your diet. Focus on consuming a well-balanced diet that includes whole grains, lean proteins, fruits, and vegetables. Limit your intake of processed sugars, saturated fats, and refined carbohydrates.
- Regular Exercise: Engaging in regular physical activity can significantly impact your diabetes management. Aim for at least 150 twinkles of moderate aerobic exercise, similar as brisk walking or cycling, each week. Exercise helps improve insulin sensitivity, control weight, and lower blood sugar levels.
- Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight is crucial for managing type 2 diabetes. Extra weight can worsen insulin resistance and increase the threat of complications. Consult with a healthcare professional to determine a suitable weight loss plan adjusted to your requirements.
Medications for Type 2 Diabetes Treatment
- Oral Medications: Many individuals with type 2 diabetes benefit from oral medications that help lower blood sugar levels. These medications work by improving insulin sensitivity, reducing glucose production in the liver, or increasing insulin secretion.
- Injectable Medications: In some cases, when oral medications aren’t sufficient, healthcare providers may prescribe injectable medications. These include non-insulin injectables and insulin therapy, which can help maintain stable blood sugar levels.
- Insulin Therapy: For individuals with type 2 diabetes who cannot regulate their blood sugar levels with oral or injectable medications, insulin therapy becomes essential. Insulin can be administered using injections or insulin pumps.
Expert Advice: Managing Type 2 Diabetes
- Regular Blood Sugar Monitoring: Monitoring your blood sugar levels regularly is crucial for managing type 2 diabetes. Maintaining a log of your readings helps you identify patterns and make necessary adjustments to your treatment plan.
- Routine Medical Check-Ups: Track your progress, and make adjustments to your treatment if needed.
- Education and Support: Seek out educational resources and support groups that can provide valuable insights into managing type 2 diabetes. Surrounding yourself with a supportive community can make a significant difference in your overall well-being.
Type 2 Diabetes Food List:
The Importance of a Healthy Diet
By making smart food choices, you can control your blood sugar levels, maintain a healthy weight, and reduce the risk of developing long-term complications. Furthermore, adopting a well-balanced diet ensures you receive a wide range of nutrients to support overall well-being.
Type 2 Diabetes Food List
A type 2 diabetes food list is a comprehensive guide that outlines the best choices for individuals with type 2 diabetes. By focusing on foods that won’t cause blood sugar spikes and provide essential nutrients, this list aims to assist in meal planning and making informed dietary decisions.
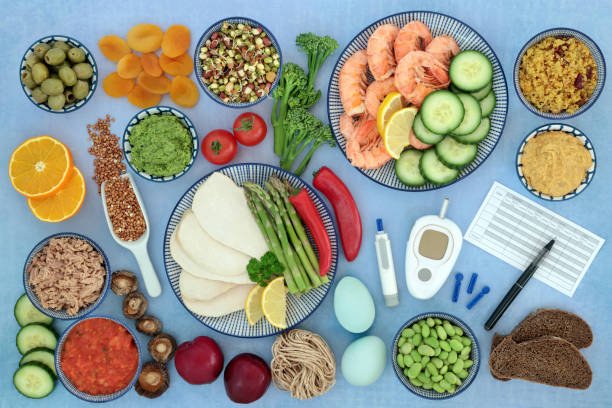

What to Include in Your Type 2 Diabetes Food List
1. Fibrous Foods
Foods rich in fiber are beneficial for individuals with type 2 diabetes as they help regulate blood sugar levels and improve digestion. Include the following in your type 2 diabetes food list:
- Whole grains (oats, quinoa, brown rice)
- Fruits (apples, berries, citrus fruits)
- Vegetables (leafy greens, broccoli, carrots)
- Legumes (chickpeas, lentils, black beans)
- Nuts and seeds (almonds, chia seeds, flaxseeds)
2. Lean Protein
Protein plays a crucial role in managing blood sugar levels and promoting satiety. When constructing your type 2 diabetes food list, consider including the following protein sources:
- Skinless poultry (chicken, turkey)
- Fish (salmon, trout, sardines)
- Lean cuts of meat (beef, pork)
- Tofu and tempeh
- Greek yogurt and cottage cheese
3. Healthy Fats
Incorporating healthy fats into your diet can help improve insulin sensitivity and reduce the risk of heart disease. Add these healthy fats to your type 2 diabetes food list:
- Olive oil
- Avocados
- Nuts and seeds
- Fatty fish (salmon, mackerel)
4. Low-Glycemic Index Foods
Foods with a low glycemic index (GI) have a minimal impact on blood sugar levels. Including these foods in your type 2 diabetes food list can help maintain stable glucose levels throughout the day. Some examples of low-GI foods include:
- Steel-cut oats
- Quinoa
- Sweet potatoes
- Berries
- Non-starchy vegetables
Diet
Foods to Limit or Avoid
While creating a type 2 diabetes food list, it’s important to know which foods to limit or avoid to maintain healthy blood sugar levels. These include:
- Refined carbohydrates (white bread, sugary cereals)
- Sugary beverages (sodas, energy drinks)
- Processed meats (sausages, bacon)
- High-fat desserts (cakes, cookies)
- Alcohol

Tips for Meal Planning
Creating a type 2 diabetes food list is just the first step – implementing it into your daily routine is equally important. Here are some practical tips for meal planning:
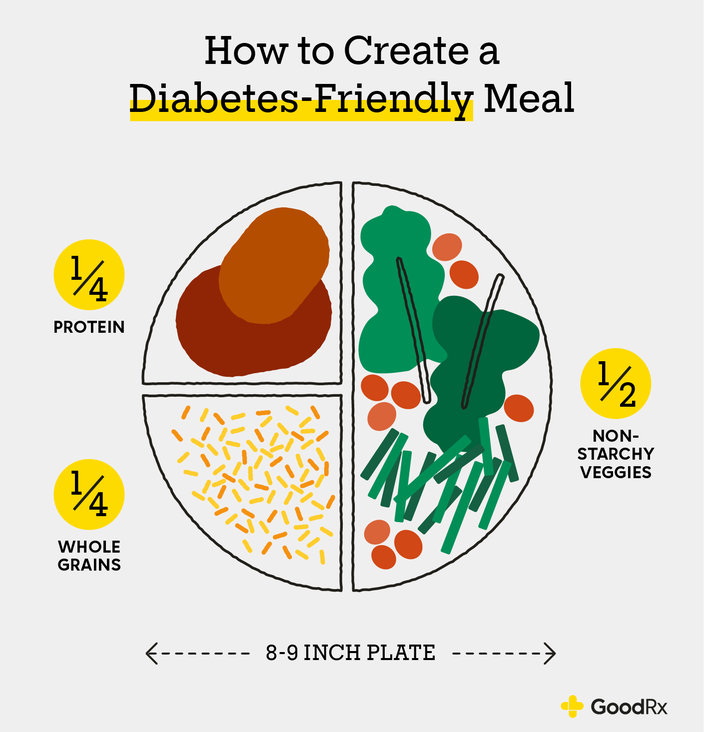
- Balance your plate: Fill half of your plate with non-starchy vegetables, one-quarter with lean protein, and one-quarter with whole grains or starchy vegetables.
- Choose healthy cooking methods: opt for grilling, baking, steaming, or sautéing instead of frying to reduce added fats and calories.
- Read food labels: Pay attention to serving sizes and the amount of sugar and carbohydrates in packaged foods.
- Mind your portions: Even healthy foods can impact your blood sugar if consumed in excessive amounts. Be mindful of portion sizes.
- Stay hydrated: Drink plenty of water throughout the day to stay hydrated and help flush out toxins.
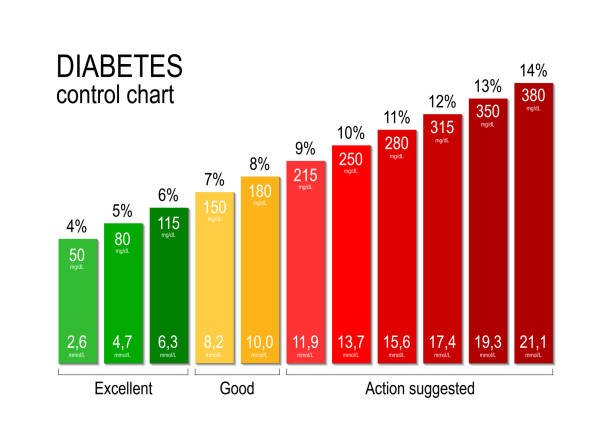
Type 2 Diabetes Range: Understanding and Managing Blood Sugar Levels
Blood Sugar Range for Type 2 Diabetes
To understand blood sugar range, it’s important to be aware of the terms used to measure it. Glucose is the primary sugar carried through the bloodstream and serves as the main energy source for the body. The following measurements provide a helpful reference for managing blood sugar levels:
- Fasting Blood Sugar (FBS): This measurement is taken after an overnight fast and provides insights into the body’s ability to control blood sugar without external influences, such as food or medication. A range of 70-130 mg/dL (3.9-7.2 mmol/L) is generally considered healthy for individuals with type 2 diabetes.
- Postprandial Blood Sugar (PPBS): Also known as post-meal blood sugar, this measurement is taken two hours after a meal to assess how the body responds to food intake. Keeping PPBS levels below 180 mg/dL (10.0 mmol/L) is typically recommended to prevent blood sugar spikes.
- HbA1c: This test provides an overall picture of blood sugar control over a span of three months. It measures the chance of hemoglobin that’s overlayed with sugar. The target HbA1c level for individuals with type 2 diabetes is generally below 7%.
Maintaining Optimal Blood Sugar Range
Achieving and maintaining a healthy blood sugar range requires a multifaceted approach. Here are some techniques that can help:
- Dietary Modifications: Adopting a balanced diet rich in whole grains, lean proteins, fruits, and vegetables can help regulate blood sugar levels. Limiting the intake of sugary and processed foods is also crucial. Consult a registered dietitian for personalized meal plans suited to your specific needs.
- Regular Exercise: Engaging in physical activity helps the body utilize glucose effectively and improves insulin sensitivity. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise, such as brisk walking, every week.
- Medication and Insulin Therapy: Depending on the individual’s condition, medication or insulin therapy may be prescribed. It is essential to take prescribed medication as directed and understand the potential side effects.
- Monitoring and Tracking: Regular blood sugar monitoring will enable you to understand how your body responds to different foods, activities, and medications. By keeping a record of your readings, you can identify patterns and make informed decisions to maintain optimal blood sugar levels.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: Can I still enjoy foods I love while managing my blood sugar levels?
A: Yes! With proper meal planning and moderation, you can still indulge in your favorite foods. Consult a dietitian to find suitable alternatives and portion sizes.
Q: How often should I check my blood sugar levels?
A: It is recommended to monitor blood sugar levels as per your healthcare provider’s advice. Typically, individuals with type 2 diabetes check their levels at least once or twice a day.
Q: Can exercise help in managing blood sugar levels?
A: Absolutely! Regular physical activity enhances insulin sensitivity, making it easier for the body to regulate blood sugar levels.
The Impact of Age on Type 2 Diabetes
What is the typical age for developing type 2 diabetes?
The risk of developing type 2 diabetes generally increases with age. Middle-aged and older individuals are more likely to experience the onset of this condition. Statistics suggest that people over the age of 45 are at a higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes compared to younger individuals.
Why does age affect the risk of type 2 diabetes?
The relationship between age and type 2 diabetes can be attributed to several factors. As we age, our body’s ability to produce and use insulin declines. This phenomenon, known as insulin resistance, can lead to elevated blood sugar levels and eventually result in type 2 diabetes. Additionally, age often comes with weight gain and a decline in physical activity, both of which are significant contributors to the development of the condition.
Age-related Risk Factors for Type 2 Diabetes
How does aging impact insulin production?
Insulin production tends to decrease with age due to various factors, including changes in pancreatic function and increased fat deposition. The decline in insulin production can lead to impaired glucose metabolism and an increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes. As individuals age, it is essential to monitor blood sugar levels regularly and make necessary lifestyle modifications to mitigate this risk.

Does family history play a role in age-related type 2 diabetes?
Yes, family history plays a crucial role in age-related type 2 diabetes. If you have immediate relatives, such as parents or siblings, with type 2 diabetes, your risk of developing the condition is higher. Genetic factors can influence insulin resistance, making it more likely for individuals with a family history of diabetes to develop the condition as they age.
Can lifestyle choices impact the risk of type 2 diabetes at any age?
Absolutely! Regardless of age, lifestyle choices can significantly impact the risk of developing type 2 diabetes. Unhealthy eating habits, physical inactivity, and excessive weight gain can exacerbate insulin resistance and increase the likelihood of developing the condition. Conversely, adopting a balanced diet, engaging in regular exercise, and maintaining a healthy weight can help prevent or manage type 2 diabetes, regardless of age.
Type 2 Diabetes food chart